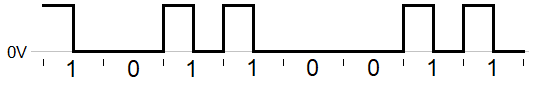- R.##
- The R series of CCITT recommendations includes R.31 and R.35-38, all of which are FDM-style VFTs (obsolete) using FSK, and R.101, a 46-channel TDM data system.
- R4#00
- A 1990s SGI/Mips Technologies RISC microprocessor architecture. Family members include the R4000, R4400, R4200, R4600, and R10000.
- RAD
- Rapid Application Development. The use of IDE programs that produce code from visual input, e.g., Microsoft Visual Studio.
- radar
- Radio Detection And Ranging.
- radiosonde
- From sonde, a sounding line (French). A balloon-borne instrument that measures and transmits meteorological data – called raob, or radiosonde observations – while rising through the atmosphere. Once the balloon bursts due to continuous expansion as external pressure drops, the unit descends by parachute for recovery and re-use.
- A rawinsonde (radio wind sonde) includes a radar reflector to make it a good marker of wind speed & direction. There’s also the dropsonde, which is dropped from an aircraft and descends by parachute while taking measurements.
- RADSL
- Rate-Adaptive Digital Subscriber Line. See DSL.
- RAID
- Redundant Array of Independent (originally Inexpensive) Disks. A technology that automatically stores data across multiple hard drives or multiple disk partitions instead of a single location, to protect against loss. This is not quite the same thing as file backup. The traditional hardware RAID is managed by a controller – a dedicated processor. A software RAID implementation doesn’t require a separate controller, and is cheaper but less reliable. There are different levels of RAID implementation, numbered 0 to 7, 10, and 0+1.
- rails
- In RF modulation, the binary data lines carrying the serial bits that determine the symbols transmitted. A QPSK signal, for instance, has 2 bits/symbol, hence 2 rails, referred to as I and Q. Bits from each rail are combined to produce one of four symbols 11, 10, 01, or 00, which in turn is represented by one of four transmit waveforms. The rails usually draw on a single source bit stream, but each can carry a separate bit stream if desired.
- rainbow table
- See hash.
- RAM
- Random Access Memory. Computer memory that, unlike the long-obsolete sequential memory, assigns data to electronically mapped locations so that it can be retrieved selectively with commands sent via an address bus. Memory capacity is often described with the ## × ## notation, meaning some number of addressable memory locations with each having the given bit size. For example, 4K × 16 means 4096 16-bit locations.
- RAM technologies can be broadly classed as either VRAM (V = volatile, meaning it loses all stored data when power is off) or NVRAM (NV = non-volatile, meaning it maintains state without power).
- The biggest use of volatile memory is as PC main memory, which comprises a very large family of technologies described separately as dynamic RAM (DRAM). The video RAM (VRAM) used on graphics cards is also DRAM, or DRAM variants redesigned for video applications. Then there’s static RAM (SRAM), used in high-speed CPU caches. Volatile types under development as of 2015 include T-RAM and Z-RAM, but most memory research is pursuing non-volatile technologies.
- The original non-volatile memory was EEPROM. SRAM with battery backup is considered non-volatile too, although that’s a bit of a cheat. Newer non-volatile types such as flash memory, FRAM, MeRAM, MRAM, NRAM, OUM, PCM, and 3D XPoint use different technologies to retain data entirely without power.
- Rambus
- The manufacturer of DRDRAM (or just RDRAM), an Intel-supported proprietary DRAM type introduced in the late 1990s. Rambus filed some unpopular lawsuits claiming patent infringement by the JEDEC-approved open standards SDRAM and DDR SDRAM.
- ramjet
- A jet engine with no moving parts. It burns fuel using oxygen from an air intake, with inlets shaped to slow the air down. This requires a speed of at least 400 mph. As in a rocket, propulsion comes from the expansion of heated gases. The aircraft saves a lot of weight because it doesn’t need to carry oxygen along with the (typically hydrogen) fuel, but it’s not a fuel-efficient design.
- RAN
- Radio Access Network. A network linked by radio signals rather than by cables, such as mobile phones connecting to a cell tower or computers connecting to a Bluetooth hub. See O-RAN.
- raob
- See radiosonde.
- RARP
- Reverse Address Resolution Protocol.
- RAS
- Row Address Strobe. See DRAM.
- Raspberry Pi
- A brand of single-board computer launched in 2012 by the non-profit Raspberry Pi Foundation, intended for use in teaching programming and computer science. The original Raspberry Pi has a low-power ARM microprocessor, discrete GPU, 256 MB to 1 GB of memory, a slot for SD card removable storage, general-purpose I/O pins, and standard ports for video, audio, USB devices, and Ethernet. It boots from the SD card and runs any of several operating systems. Compare Arduino.
- The foundation’s commercial arm and its imitators have since developed many newer versions, variants, and accessories.
- raster
- From Latin rastrum, a rake. Refers to display technologies that use a rectangular grid of dots or pixels, writing or setting them line by line. All current (2015) monitor, print, and scan technologies are raster-based, although most of the computer graphics technologies that use them are based on the older but more flexible vector graphics.
- RAT
- Remote Access Tool. A program, e.g. SSH or Telnet, for controlling and monitoring a computer remotely over a network. RATs have legitimate uses, but are also used by some malware programs. In the latter case, the term is usually defined as Remote Access Trojan.
- rawinsonde
- See radiosonde.
- Rayleigh fading
- Named for British physicist John W. Strutt, Lord Rayleigh (1842-1919). Another name for multipath RF interference.
- Rayleigh scattering
- Named for British physicist John W. Strutt, Lord Rayleigh (1842-1919). Scattering caused by spherical particles whose radii are much smaller than the wavelength of the scattered radiation. Best known as the reason the sky is blue: the intensity of scattered light is inversely proportional to the fourth power of its wavelength, so blue light is affected much more than red.
- RB
- Information bit rate.
- RBHC
- Regional Bell Holding Company. See divestiture.
- RBOC
- Regional Bell Operating Company. A confusing name for what is more properly called just a Bell Operating Company (BOC). See divestiture.
- RC
- (1)
- Resistor-Capacitor. A simple resonant circuit incorporating these two elements.
- (2)
- Raised Cosine. See RRC, windowing.
- RC4
- Ron’s Code #4. See encryption.
- RCA
- Radio Corporation of America. A major electronics manufacturer, broken up in 1986, but see cable connector.
- RCD
- Residual Current Device. Same thing as a GFI.
- RCLED
- Resonant Cavity Light-Emitting Diode. An LED in a resonant optical cavity. Similar to a VCSEL, but with a less reflective mirror as the output coupler.
- RCS
- Rich Communications Services. Also referred to as Chat, this is an industry standard messaging protocol introduced in 2002 primarily for mobile phones. Unlike the older SMS, it can carry multimedia content, and doesn’t have a technological limit on message length. It drops back to SMS if the network or other-end device doesn’t support RCS.
- RDBMS
- Relational Database Management System. A database management system that incorporates the relational data model, i.e., data is organized and accessed according to the relationships between data items. These relationships are expressed as tables, and table interdependencies are expressed by data values rather than pointers. A RDBMS normally includes a SQL API.
- RDE
- Rotating Detonation Engine. A refinement of the pulse detonation engine that causes the point of combustion to rotate around the inner circumference of the chamber. It has the potential to be both lighter and more efficient than other engines, but is tricky to engineer.
- RDF
- (1)
- Resource Description Framework. A suite of W3C specifications for presenting metadata (information about a resource), to exploit the capabilities of XML.
- (2)
- Radio Direction-Finding. Determining the physical location of an RF transmitter by triangulation of its signal.
- RDIMM
- Registered DIMM. See DRAM.
- RDRAM
- Rambus DRAM. See Rambus, DRAM.
- RDS
- Source-to-drain resistance. The figure that determines a MOSFET’s maximum current rating and power consumption.
- reactance
- The capacitive or inductive component of impedance.
- reactor
- Meaning nuclear fission reactor, an installation for generating heat from a controlled chain reaction of the fission of heavy elements, then using that heat to boil water to drive steam turbines, and, finally, using the rotating turbines to generate electricity. The first reactors used the same fuel materials as atomic bombs, though with lower levels of refinement. Some reactor design approaches:
- breeder reactor – A design that uses Pu-239 fuel cores surrounded by U-238 jackets. Neutrons from the fuel cores bombard the jackets to create more Pu-239, so the reactor ultimately produces more fuel than it uses. It has liquid sodium coolant because that doesn’t slow down the neutrons as much as water would. Breeder reactors are more expensive than water-cooled designs.
- LWR – Light Water Reactor. The standard for US nuclear power plants, using ordinary water rather than heavy water as the coolant and moderator to slow down neutrons emitted by ~3% enriched uranium-235 fuel rods. This slowing increases the number of neutrons that are captured by neighboring U-235 atoms, triggering the fission that generates heat. Sub-types include the boiling water reactor (BWR), which uses the moderator/coolant to also generate the steam driving the turbines, and the more common pressurized water reactor (PWR), which keeps the moderator/coolant in a closed loop and has a separate water cycle for the turbines.
- MSR – Molten Salt Reactor. Uses a liquid fuel of fissile materials dissolved in molten salts, which are kept molten by the heat of fission, and drain into a holding tank if the reactor encounters problems. Because the salts have a much higher boiling point than water, they don’t need the expensive, potentially hazardous pressurization used for water-based reactors.
- SFR – Sodium-cooled Fast Reactor. Designed to consume nuclear waste as fuel, it uses liquefied sodium to absorb heat from the reactor core and transfer it to a boiler chamber, producing steam to drive the turbines. Sodium has greater heat capacity than water, can be maintained at lower pressures without vaporizing, and doesn’t corrode steel. Still in development as of 2014.
- SMR – Small Modular Reactor. A type of relatively small, low-power (typically 30 to 300 MW) fission reactor that can be manufactured in one place and assembled in another, taking advantage of economies of manufacturing scale while offering greater flexibility and a much smaller footprint than a traditional power plant. There are many different designs, only a few of which are in actual use as of 2023.
- TWR – Traveling Wave Reactor. Newer name for a type of power plant that slowly generates its fuel from a variety of low-grade fissile materials, including depleted uranium, and slowly consumes it at the same rate. It’s more properly a standing wave reactor, as the idea is to maintain the fuel-generation and fuel-burn waves in the same physical spot within the reactor by adjusting the composition and placement of the fissile materials being fed in.
- real mode
- The operating mode of the earliest x86 processors, the 8088 and 8086. It uses 16-bit instructions and 20-bit memory addressing, meaning no more than 220 = 1,048,576 bytes (1 MB) of RAM. The 80286 supports real mode, but also has protected mode, allowing it to access extended memory.
- Later processors have other modes – 32-bit protected mode, virtual real mode, 64-bit extension mode – but all x86-compatible CPUs still start in real mode to retain backward compatibility.
- rectifier
- A device that converts AC to DC. Modern designs use solid-state circuits rather than the old high-speed mechanical switches or the even older mercury arc rectifiers, and apply filtering to smooth the output waveform, but don’t ensure constant voltage the way an AC-DC regulator does.
- A half-wave rectifier converts just half of each AC sine wave to output DC current. The more complex full-wave rectifier, as its name suggests, uses the entire cycle.
- Along with the single-phase types found in some consumer electronics, there are industrial three-phase rectifiers.
- The complementary device, for converting DC to AC, is the less efficient inverter.
- red team
- From military wargames, where Blue Force is our side and Red Force is the enemy (or OpFor, opposing force). A group tasked to operate independently in the role of attacker to provide a realistic security test of software, a network, a physical installation, etc.
- Reed-Solomon
- Named for its developers, Irving Reed and Gustave Solomon (MIT Lincoln Laboratory). A type of non-binary block code that operates on m-bit symbols rather than on bits. Because it corrects bad symbols without regard to which symbol bits are bad, it actually performs better with burst noise than with random noise. That’s why it concatenates so well with convolutional codes. See FEC.
- refactoring
- Referring to software, this is the iterative, organized process of restructuring an application’s source code to improve efficiency and re-usability without changing its external behavior. There are refactoring tools to automate the process.
- ReFLEX
- A variant of Motorola’s FLEX family of paging protocols, to provide two-way text messaging. ReFLEX 25 uses a 4-FSK carrier at 1.6, 3.2, or 6.4 kb/s. An outbound (to the customer) channel is 25 kHz or 50 kHz wide, accommodating one or three carriers, respectively. The 50 kHz channel can transmit up to 12.8 kb/s. Outbound channels operate in the 930-931 or 940-941 MHz band. Inbound channels (901-902 MHz) are 12.5 kHz wide, and transmit up to 9.6 kb/s. ReFLEX 50 doubles the maximum outbound channel rate to 25.6 kb/s.
- reflow
- (1)
- The process of melted solder flowing onto a circuit board to fuse components in place. This occurs at around 220° C to 240° C, with lead-free solders at the high end (see eutectic). A component that can briefly stand these temperatures is called “reflowable”.
- (2)
- The unwanted shifting of text that occurs when a digital document is transferred to a new format.
- ReFS
- Resilient File System. A file system introduced with server versions of Windows 8.
- regex
- Regular Expression. A string of characters describing a sequence to search for when the sequence is variable or not precisely known. For example, the regex could specify multiple spellings of a word, and the search would look for any of them. A regex engine is needed to interpret regexes. Most Internet search engines have them. So do many programming language compilers and interpreters. The PERL format rules for regexes have been very influential.
- For example,
[+-]?(([0-9]+\.?[0-9]*)|(\.[0-9]+))is a regex matching any valid number written in standard form, because it requires a sequence that begins with + or - or neither; that contains at least one digit; and that contains either no decimal point, or a single decimal point in any position. That means it will identify character strings such as 17.935, +10, -0.0116, 42, .250, etc. as matches. A bare-bones explanation of the symbols used: - The brackets [] enclose exact characters to look for, with enclosed dash - indicating a range between the character before it and the character after it
- The parentheses () indicate order of execution the way they do in mathematics
- ? means match the preceding sequence 0 or 1 times
- * means match the preceding sequence 0 or more times
- + means match the preceding sequence 1 or more times
- \ is an escape character requiring special interpretation of the character following it; for example, \d would mean any digit, but \. means just a period
- | means use either the sequence before it, OR the sequence after it, but not both
- To have the regex treat one of those characters literally, meaning make it part of the sequence being searched for, precede it with the escape character \ (a backslash). Do the same for the single-quote and double-quote characters ' and " to prevent them from being treated as delimiting characters for the search string.
- regression testing
- A regression is a bug that appears in previously validated software following a change to some other part of the system, including drivers, hardware components, or other code. Regression testing seeks to catch such bugs before release.
- regular expression
- See regex.
- regulator
- A voltage regulator provides a controlled and nearly constant output from some less reliable power input. There are AC-AC, AC-DC, and DC-DC regulators. (The AC-DC regulator differs from the simpler rectifier in that it keeps output voltage level constant.) They’re used in everything from power-plant transformers to cell-phone chargers. Some incorporate an isolation transformer to separate source ground from load ground. Two common classes of DC regulators, also known as converters:
- Linear regulators use a variable-resistance configuration, typically transistors operating in their linear region, to set the output level. They’re precise and simple, but can act only as voltage step-down (buck) regulators, and tend to have poor efficiency – roughly equal to the ratio of output to input voltage.
- Switching regulators (a.k.a. switching-mode power supply, or SMPS) use on-off BJT or FET switches, running at speeds of 10 kHz to several MHz, to transfer current in discrete packets to the output. Depending on the design and application, they act as buck, step-up (boost), or inverting regulators. They’re more efficient than linear types, especially at lower switching frequencies. On the down side, they introduce significant noise into the power. Switching sub-types include the inverting buck-boost regulator (produces a fixed, opposite-polarity output), the Cúk regulator (an optimal inverting buck-boost design, pronounced “chook”), the forward regulator (isolated buck), the flyback regulator (isolated buck-boost, with the isolation transformer also acting as the current-storage element), and the SEPIC regulator (non-isolated, non-inverting buck-boost that compensates for falling input voltage).
- remailer
- Usually means an anonymizing remailer, a type of proxy server that forwards the E-mail of its users to the intended destinations while withholding true source addresses. There are different types, offering varying levels of protection for user anonymity. Remailer users commonly send their messages through a chain of them in case one is compromised.
- resistor
- An electronic component that impedes the flow of current. Resistance R is measured in ohms (Ω). Resistors in series add, but resistors R1 and R2 in parallel provide a resistance R = R1R2 / [R1 + R2]. Types include carbon composite, wire-wound, and metal-film resistors. At higher frequencies, carbon composite types might exhibit unacceptable parasitic capacitance, and wire-wound resistors have high inductance.
- The most common means of marking resistors is a four- (or five-) stripe color code. The first two (or three) stripes, starting at the stripe nearest to the lead, indicate the numeric value of the resistor according to the code:
- The third (or fourth) stripe is the value by which the numeric value is multiplied: yellow = 10000, orange = 1000, red = 100, brown = 10, black = 1, and gold = 0.1. The fourth (or fifth) stripe is the tolerance of the resistor, i.e. the amount by which its actual resistance can vary: gold = 5% and silver = 10%.
- REST
- REpresentational State Transfer. A standard style of application programming interface (API) introduced in 2000 for Web development, and commonly applied through the OpenAPI Specification (OAS). It uses a HTTP-based data format, and is designed to be lightweight and scalable. Servers employing REST APIs respond to client queries with a representation of the source material that enables the client to then retrieve the actual source. The point is that the source material can be updated without requiring any change to how the client requests it. Compare SOA.
- The RESTful API style is an extension of REST with additional features, including making JSON part of the data format.
- RF
- Radio Frequency. Electromagnetic (EM) waves in frequency ranges that can be electronically modulated for communications purposes. In the US, the RF spectrum is usually defined as shown below. The names for bands below 3 kHz aren’t universal. Some sources call 0-30 Hz Ultra Low Frequency (ULF), 30-300 Hz Extremely Low Frequency (ELF), and 300-3000 Hz Voice Frequency (VF). Others call everything below 30 kHz Audio Frequency (AF), or just don’t include it in the RF spectrum, since it has few communications uses. The microwave band is a portion of the RF spectrum from about 2300 MHz up.
- Frequency of a RF carrier wave is inversely proportional to the size of the antenna needed to transmit it, and directly proportional to the maximum bandwidth it can carry. That is, lower frequencies require bigger antennas and send less information. However, frequencies in the HF range and below have the useful property of being reflected by the ionosphere, so they propagate far beyond line of sight, potentially circling the globe. Also, attenuation by water is inversely proportional to wavelength, which is why submarine communications employ frequencies as low as SLF despite the huge, inefficient antennas and the very low data rates: the signals can penetrate deep under water.
- Terahertz (THz) radiation, or T-rays, means EM waves from roughly 300 to 10,000 GHz. Despite very strong atmospheric absorption, terahertz RF has potential for surface-penetrating radar, high-resolution imaging, and short-range communications. The difficulty is that it’s too high-frequency for conventional electronics but too low-energy for photonic (optical) devices – the so-called terahertz gap. One known approach to THz comms uses two lasers at frequencies F1 and F2, one of them modulated. Shine them on a photodiode, and output the |F1 - F2| component of the diode’s response to an antenna.
- RFC
- Request For Comments. A memo seeking input from the computer networking research community on Internet problems and topics. Steve Crocker at UCLA issued RFC 1 on 7 April 1969, looking for comments on the software of the fledgling ARPAnet.
- RFI
- (1)
- Radio Frequency Interference. Same as EMI.
- (2)
- Request For Information. An exploratory step in the federal procurement process, to solicit ideas from industry for buyers who don’t know what’s available or exactly what they want. Compare RFP, RFQ.
- RF-I
- Radio Frequency Interconnect. New method to overcome the problems created by ever-shrinking electronic components: Using wireless RF rather than electrical signals to link parts of a circuit or even a chip.
- RFID
- Radio Frequency Identification. Any of several short-range tagging-and-tracking technologies. Not all of them rely on RF, so they’re also called automatic identification and data collection (AIDC) or dedicated short-range communication (DSRC). A small tag is attached to the item to be tracked; a radio or magnetic reader detects the signature of the tag, and, by extension, the presence of the tagged item. The US government and large retailers use mid-range RFID at the case and pallet level for inventory tracking. RFID is a major concern to privacy activists.
- Researchers have created a technology to counter the kind of fraud in which a RFID tag is removed from the original item and attached to a cheap knockoff: attach the tag with a thin layer of glue containing microscopic metal particles, and scan it with a THz-frequency reader. The metal particles give the RF reflection from each tag a unique fingerprint that will be destroyed if the tag is removed.
- Passive tags are the smallest and cheapest. As the name implies, they have no battery or other power source. They’re read by a very short-range transceiver that either generates an RF signal and detects the reflection from the tag (like a radar with a passive transponder), or creates a magnetic field and senses the inductive effects of the tag (see NFC). Typical commercial systems operate at 125 kHz or 13.56 MHz, and have read distances of as little as 1 cm or as much as 10 meters. Placed on individual retail items, they record sales and prevent theft. The simplest kind, with one erasable bit, is the electronic article surveillance (EAS) tag. When the store clerk passes your new jacket over the scanner, its EAS tag is erased, so that the reader at the front door won’t sense it and trigger an alarm. As of 2006, there are passive tags as small as a grain of sand (0.4 mm) with 128 bits of data storage. The problem with making them even smaller is the need for an antenna. Extremely high frequencies (as much as 60 GHz for transmission as of 2014) permit ultra-tiny antennas, but mandate short range.
- Semi-passive tags have a processor supported by a small battery, but still rely on power from the reader to transmit. They have more range than the passive tags, and the ability to report data from a sensor.
- Active (transponder) tags have the longest read range (starting at ~30m, but potentially much more), thanks to internal batteries for powered transmission, more data storage/processing, and write as well as read capability. This makes them the largest and most expensive type. In the US, they’re used for automated toll collection and railroad-car tracking, and mostly operate at 902-928 MHz or 2.4-2.4835 GHz.
- RFP
- Request For Proposal. The stage of the federal procurement process prior to actual contract award, from buyers who know what they want and have requirements ready. Requirements declare what a system shall do, not how it shall do it. Specifications, often confused with requirements, set bounds and targets for the expected performance of a system. Compare RFI, RFQ.
- RFQ
- Request For Quotation. A more advanced stage of the federal procurement process, accompanied by formal requirements and specifications. Also called a request for bid (RFB). Compare RFI, RFP.
- RG##
- Registered (or Radio frequency Government) ##. A series of braided coaxial cable standards for video and antenna signals. The numbers indicate the order in which the standards were registered. Common types include RG8, RG58, RG174, RG188, RG213, RG214, and RG316, all with 50 Ω characteristic impedance; RG6, RG11, and RG59, with 75 Ω; and RG-62, with 93 Ω. MIL-STD extensions such as /U, A/U, /CU, and /X are used to indicate different constructions, with different efficiencies.
- RGB
- Red Green Blue. Another name for the long-obsolete CGA graphics. Also refers to the use of LEDs with these three colors to produce decorative (i.e., serving no functional purpose) light displays on electronics, especially parts in custom-built PCs.
- RH
- Relative Humidity. The ratio of the current partial pressure of water vapor to the saturation vapor pressure. Rising temperature or atmospheric pressure increases the saturation vapor pressure (often described, vividly but inaccurately, as “the amount of water vapor the air can hold”). This initially causes RH to fall. However, by increasing evaporation rate, it eventually boosts partial vapor pressure as well and causes RH to start rising. Precipitation can and routinely does occur at RH less than 100%, and, conversely, 100% RH doesn’t mean it’s raining. See dew point.
- Rhapsody
- See Mac OS.
- RHCP
- Right-Hand Circular Polarization. See polarization.
- rheostat
- Similar to a potentiometer – that is, a tunable resistor. It has just two contacts rather than three. One is a sliding contact to vary the effective length of the resisting element.
- RIC
- RAN Intelligent Controller. A proposed (2021) component of mobile telephony that will monitor multiple base stations and reconfigure them in real time to maintain optimum system performance of their radio access network (RAN).
- right ascension
- See equatorial system.
- right-hand rule
- A convention for describing combined linear and rotary motion. Grasp an object in the right hand, and rotate it in the direction the fingertips are pointing. If the object simultaneously moves perpendicular to this rotation in the direction of the thumb, it exhibits right-handed rotation. If it moves in the opposite direction, that’s left-handed rotation.
- By tradition, most spiral-threaded mechanical objects – nuts and bolts, bottles and bottle-caps, light-bulbs and sockets, faucets and hose couplings – have right-handed threading. The much less common left-handed threading is reserved for special uses, mostly to prevent accidental unscrewing by left-handed rotations, e.g., toilet flush handles and the right pedals of bicycles.
- The right-hand rule also appears in vector mathematics, and therefore in the physics of electric/magnetic fields and EM waves. Given two vectors X and Y at right angles (orthogonal) to one another, their cross product is a third vector Z at right angles to both of them, with its direction set by the right-hand rule with rotation from X to Y.
- RIMM
- Trademark name for the Direct Rambus DRAM module, which resembles a DIMM but isn’t an open standard. Not to be confused with RDIMM (registered DIMM). It’s 5.25" × 1.25" (height varies), with a metal shield enclosing the module’s memory chips. The 16-bit RIMM has 184 contacts divided into groups of 92 by two notches – one centered, one off center – in the bottom edge. The 32-bit RIMM has a more dense array of 232 contacts.
- RIP
- Routing Information Protocol. Part of the TCP/IP protocol suite at the Application layer. Allows gateways to periodically broadcast their current routing tables to connected hosts and networks.
- RIR
- Regional Internet Authority. Any of four non-profit groups that register IP addresses with ICANN for their part of the world. The American Registry for Internet Numbers (ARIN), in Chantilly, VA, is the one that covers North America, parts of the Caribbean, and sub-equatorial Africa. The other three are the Asia Pacific Network Information Centre (APNIC), the Latin-American and Caribbean IP Address Registry (LACNIC), and Réseaux IP Européens (RIPE NCC). Each RIR obtains blocks of IP addresses from ICANN, and in turn parcels them out to local and national Internet authorities (LIRs and NIRs), or directly to ISPs.
- RIS
- Reconfigurable Intelligent Surface. A digitally controlled panel that electronically adjusts its surface properties to change the phase and direction of an RF signal that it reflects or refracts. Still experimental as of 2022, it can boost directional gain of transmitting and receiving antennas at modest cost. The main difficulty is the RIS controller knowing which surface properties are needed, moment to moment, in a constantly changing RF environment.
- RISC
- Reduced Instruction Set Computing. A microprocessor design concept starting in the 1980s that uses fewer and simpler machine-language instructions than the older CISC, and therefore has a less complex processor architecture. This shifts some of the complexity to software, meaning larger applications but faster processing.
- ARM and other RISC designs have gained widespread acceptance, but, as the CISC entry explains, the distinction has lost importance.
- RISC-V (“risk-five”) is a free, open-source ISA released in 2014 with just 47 core instructions, maintained by a non-profit organization called RISC-V International. It’s modular – that is, much of its functionality comes from a set of optional extensions, so CPU designers incorporate only the ones they need. Implementations of RISC-V follow the naming convention “RV##xxx”, where ## is the bit width (32 or 64) of the internal data bus and xxx is a set of letters identifying the extensions that the design uses.
- RJ##
- Registered Jack. Any of the USOC modular plug/jack wiring standards, such as RJ11, RJ14, and RJ45.
- RLC
- Resistor (R), Inductor (L), Capacitor (C). A passive resonant circuit, typically a filter, that includes these three elements. Also called a second-order circuit, since a second-order differential equation describes voltage or current through it. See tank circuit.
- RLS
- Recursive Least Square. An adaptive noise-canceling filter algorithm.
- RMA
- Return Merchandise Authorization. In the PC components business, a form for explaining why a part is being returned for a refund or replacement.
- RMS
- (1)
- Root Mean Square. The square root of the average of the squares of a given set of numbers. For a sinusoid, such as an AC voltage V0, VRMS = V0/sqrt2 ≈ 0.707[V0].
- AC power levels are commonly expressed in RMS. For example, US residential power is a sine wave with nominally ±177 V peaks, which works out to the familiar 125 V (RMS). It’s also called 120 V, 115 V, and 110 V, because actual level depends on where it’s measured. The RMS value of an AC signal corresponds to the DC level that would produce the same amount of heat in the same load. See power.
- (2)
- Richard M. Stallman. Founder and former president of the FSF, and so ubiquitous a champion of the free-software philosophy that he’s routinely referred to by his initials.
- RNG
- Random Number Generator. Modern network security depends heavily on random numbers for cryptographic keys, but software can’t generate true randomness. What an algorithm produces is pseudo-random numbers, which inevitably contain patterns. However subtle these patterns might be, they still introduce weakness into cryptographic systems that rely on the numbers.
- To fill the gap, hardware manufacturers have created RNG microcircuits. They use a physical source such as temperature readings or quantum fluctuations, and apply hash functions to compensate for non-random bias in the measurement mechanism. A newer, all-software approach uses two uncorrelated pseudo-random sources, and applies another algorithm to combine their outputs into numbers that appear genuinely random – high-quality pseudo-randomness, as the mathematicians say.
- Researchers have identified a way to undetectably sabotage a RNG at manufacture: adjust the doping of some of the transistors so that their supposedly random output bits will in fact be constants.
- robots.txt
- A file placed in the root directory of a Web site to provide instructions to Web-crawling bots on how to index the site. It depends on voluntary compliance, so it provides no protection against malbots, and it’s increasingly common for even non-malware corporations to ignore it, particularly AI companies.
- ROC
- Region Of Convergence.
- rod logic
- The still-experimental (2015) idea of implementing digital logic using MEMS components, which can be even smaller than the smallest practical transistors. Making strong mechanical parts at molecular scale is yet another potential use for graphene.
- RoHS
- Restriction of Hazardous Substances. European Union initiative to control use of six toxic materials in manufacturing: lead (Pb), mercury (Hg), cadmium (Cd), hexavalent chromium (Hex-Cr), polybrominated biphenyls (PBB), and polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDE).
- rollover cable
- A network cable that reverses the order of the pin connections between its ends: pin 1 at one end connects to pin 8 at the other, pin 2 to pin 7, etc. It’s a type of crossover cable, but not for Ethernet.
- ROM
- (1)
- Read-Only Memory. Not actually memory in the modern computing sense, but computer data storage that can be read but not changed by users. See PROM, EPROM, EEPROM, and CD-ROM. More recently, ROM can refer to a file containing a copy of the data or programming stored on an IC chip. These files are used to create copies or modified versions of video games.
- (2)
- Rough Order of Magnitude. The standard unit of measure in a WAG.
- root
- The highest level of access in Unix and related operating systems. A root account, often called admin or superuser on other types of OS, can access any file and change any system setting.
- As a verb, “to root” means hacking a system to obtain this kind of access, and most often refers to attacks by rootkit-equipped malware. However, some users root their own equipment – cellphones, media players, game systems, etc. – to remove manufacturer-imposed restrictions or unwanted features. This is also called jailbreaking (especially for Apple iPhones), or box breaking (for removing a cell phone’s country, network provider, or other SIM card restrictions). Its legality varies with the country and the device.
- Some corporations root the equipment of their customers. For example, in 2005 Sony sold music CDs that installed root-level anti-copying software on Windows PCs that played them. Beginning in 2009-2010, many vendors (including Motorola, Samsung, and HTC) shipped smartphones with rootkit spyware called Carrier IQ, apparently at the behest of mobile service providers. These practices are always legal.
- root certificate
- See digital certificate.
- rootkit
- System-administrator (root, in Unix or Linux) tools and techniques to conceal files, registry entries, memory addresses, and network connections from programs other than the one using them. They operate at the virtualized (boot-sequence replacement), kernel, library (system call), or application level. Sophisticated malware employs rootkit methods to hide.
- ROR
- Rotate Right. See binary logic.
- ROSA
- Receiver Optical Sub-Assembly. A device that provides a receive interface to a fiber line. See TOSA.
- router
- (1)
- Sometimes called a border router, this device connects one network to another – LAN to LAN, LAN to Internet, even LAN to POTS. Unlike the dumber switch or hub, a router can read protocol level (OSI layer 3) addresses as well as MAC numbers. Traditionally, it has three major functions:
- route processing – Building and maintaining a routing table, using protocols such as RIP (Routing Information Protocol) and OSPF (Open Shortest Path First). The routing table, also called an address lookup table, can get quite large – especially on the Internet.
- packet forwarding – Packets are forwarded to their destination based on paths described in routing tables. More sophisticated routers can find the best path. MAC (Medium Access Control) numbers are used to resolve addresses. An IP checksum is calculated to ensure that the packet has not been corrupted.
- special services – Translations from one protocol to another (using protocol level addresses), prioritization, packet filtering, authentication, etc.
- Security has become a fourth major function. The Web has plenty of thoughts on this, e.g., https://routersecurity.org/.
- Routers can be purpose-built for the job, or can be general-purpose computing devices configured to serve as routers. See also gateway.
- (2)
- A machine that cuts circuit boards to a programmed design.
- ROYGBIV
- Red Orange Yellow Green Blue Indigo Violet. The traditional primary colors of the visible light spectrum, in order of increasing frequency and decreasing wavelength (as seen in rainbows). Nowadays, indigo is usually excluded. See light.
- RP
- Rapid Prototyping. Quickly manufacturing physical objects from computer models. The long-established CNC approach cuts down a solid block of material, so it can work with very hard or very soft materials, from steel to styrofoam. The much newer 3D printing instead lays down a series of layers to build up the object. 3D printers are cheaper, safer, and more versatile than CNC, but are limited as of 2016 to extruded plastic and similar materials.
- RP-nnn
- Denotes a reverse-polarity version (RP) of a standard cable connector (nnn). See cable connector.
- RPM
- Revolutions Per Minute.
- RRAM
- Resistive Random Access Memory. Also ReRAM. A non-volatile RAM that electrically changes the resistance of memory cells to write a 0 or 1, and non-destructively reads them. It’s a leading competitor to replace flash memory, and other memory types as well.
- RRC
- Root Raised Cosine. A filter to eliminate ISI. A raised cosine (RC) filter has a transfer function equivalent to a half-cycle cosine wave. Its impulse response, the Nyquist pulse, has zero ISI with neighboring pulses at the sampling times. A root raised cosine filter has a transfer function that’s the square root of the RC function. Its impulse response does NOT have zero ISI at the sampling interval. However, if the transmitter uses the RRC filter and the receiver uses a matched RRC, their product is the raised cosine response, and ISI deliberately introduced at the transmitter is removed at the receiver. See windowing.
- RRI
- Rail-to-Rail Input. Referring to an op-amp, this means the capability to accept an input signal with voltage range equivalent to the difference between the op-amp’s power and ground (or negative) rails, VCC and GND (or VEE).
- RRO
- Rail-to-Rail Output. Referring to an op-amp, this means the capability to produce an output signal with voltage range equivalent to the difference between the op-amp’s power and ground (or negative) rails, VCC and GND (or VEE).
- RS
- See Reed-Solomon.
- RS-###
- RS = Registered Standard. Any of a number of serial-line data protocols originated by the EIA, and properly called EIA-### or, more recently, EIA/TIA-### (thanks, TIA). Multiple versions of each can exist. None of these standards apply bus control adjudication (flow control) – that’s up to the designer. Ports and cables for these standards commonly use D-sub connectors, mostly DE-9 and occasionally DB-25.
- RS-232 – Version A in 1967, version E in 1991. The basis for the serial port used on almost all PCs, at least until the combination of USB and wireless connections rendered it obsolete. It’s the same as the ITU-T V.24 and V.28 standards combined – V.24 covers signal names and functions, while V.28 details voltage & current limits and pin assignments. RS-232D/E signal levels are +3V to +25V (high, or binary 0) and -3V to -25V (low, or binary 1). The unbalanced signal goes up to 50 feet and 20 kb/s, or more with serial line drivers, and can link just two nodes, typically DTE and DCE. RS-232 usually uses DE-9 connectors, although standards before 232D didn’t specify hardware pinouts. 9-to-25 adapters are available, but some of them don’t connect all the pins. At a minimum, RS-232 must have Receive Data (RxD), Transmit Data (TxD), and ground (GND), which use the pins shown below for the DTE. (For the DCE, reverse the RxD and TxD pin numbers, so that DTE 2 goes to DCE 3, and DCE 3 to DTE 2. To connect two DTEs, use a crossover cable.)
- RS-422 – Uses differential (balanced) signaling, for up to 10 Mb/s at 1.2 meters or 100 kb/s at 1200 meters. With one twisted pair, it can be a half-duplex link for two nodes, like RS-232, or a simplex bus linking one driver with up to 10 receivers, like RS-423. Two 422 twisted pairs can support a half-duplex bus or full-duplex point-to-point link. For longer distances or higher data rates, put 100Ω termination resistance across each twisted pair, ideally at the receiving end, to reduce reflection noise. (The two lines of a pair are NOT a loop.) RS-422 has the same DE-9 and DB-25 pinouts as RS-485.
- RS-423 – Unbalanced like RS-232, can support a simplex bus with one transmitter and up to 10 receivers like RS-422. Runs at a maximum 100 kb/s and 1200 meters. Unlike RS-232, it has two ground references, grounded only at the transmitting end. Line levels are up to +6V for 0 and -6V for 1, referenced to transmitter ground. Usually uses DB-25 or DC-37 connectors. If asynchronous, RS-423 generally doesn’t use its control signals.
- RS-485 – Whereas the similar RS-422 can have only one driver and up to 10 receivers on a single transmission line, RS-485 can have up to 32 of each. It can run half-duplex with a single twisted pair, or full-duplex with two pairs: one dedicated TxD+/TxD- and one dedicated RxD+/RxD-. Of course, even in full duplex, only one driver sends at a time. The inactive drivers are switched off, a trick RS-422 doesn’t support. For longer distances or higher data rates, put 120Ω termination resistance across each twisted pair at each end. The standard pinouts, omitting control lines, are below. Note that manufacturers often use custom pinouts.
- RS-530 – Incorporates RS-422 (balanced) and RS-423 (unbalanced) transmission.
- RSA
- (1)
- Rivest-Shamir-Adleman. See encryption.
- (2)
- Real-time Spectrum Analyzer.
- RSFQ
- Rapid Single Flux Quantum logic. Developed in Russia in the mid-1980s for superconducting ICs with Josephson junctions. It runs at clock speeds beyond 100 GHz – possibly way beyond – while using very little power. Since it allows digital circuits to operate at RF and microwave frequencies, an obvious application is high-speed A/D conversion in digital RF modules for wireless comms and high-performance instruments. However, its dependence on superconductivity has kept commercial use impractical.
- Whereas the older Josephson latching logic tried to mimic semiconductor logic, copying the voltage level output of the transistor, RSFQ is based on the storage and transmission of quanta of magnetic flux. Within a closed section of superconducting material, magnetic flux can exist only in discrete amounts. The presence of a flux quantum (a fluxon) in a loop equals 1; its absence is 0.
- RSL
- Rambus Serial Logic. See logic family.
- RSS
- (1)
- Rich Site Summary (RSS 0.91, introduced by Netscape in 1999). Other versions are dubbed RDF Site Summary (RSS 0.9 and 1.0) and Really Simple Syndication (RSS 2.0.0). A family of XML formats for frequently updated Web pages. A RSS feed is an XML file that presents the updates.
- (2)
- Root Sum of Squares. The square root of the sum of the squares of a given set of values. Similar to RMS, with one less step, this calculation is often used to summarize sets of uncorrelated errors.
- RSVP
- Resource Reservation Protocol. A quality-enhancing protocol for improving network performance.
- RT
- Remote Terminal. A non-controlling node on a MIL-STD-1553 data bus.
- RTC
- Real-Time Clock. A digital clock that keeps track of the current year, month, day, hour, minute, and second, and provides this data to a processor. It normally has a long-life battery backup so that it retains time when system power is off. A hardware RTC, with a crystal oscillator drawing on the battery, is more accurate than a software RTC.
- RTCA
- Radio Technical Commission for Aeronautics. FAA-supported, non-profit group that develops aviation technology standards and guidelines, including safety and testing, used by government and industry.
- RTD
- (1)
- Resistance Temperature Detector. A metal lead with a coefficient of resistivity ρ that varies as a function of temperature. More accurate and expensive than a thermistor or thermocouple, with better sensitivity than the latter and wider temperature range than the former.
- (2)
- Round Trip Delay. The time between a signal or message being sent and a response coming back.
- RTE
- Run-Time Environment. Also called run-time engine or runtime system. A set of software tools, libraries, and other resources to allow a program to run. A computer’s operating system is a run-time environment, but the term usually means something loaded in addition to the OS to support a particular application.
- RTF
- Rich Text File. A relatively simple document file format created by Microsoft, and supported by most word processing software. The files carry the .rtf filename extension.
- RTFM
- Read The Manual. A pithy piece of tech-support advice, descended from the old test-taking maxim RTFQ.
- RTG
- Radioisotope Thermal Generator. A power source that uses heat from the decay of a radioactive isotope to create voltage from a thermoelectric material. It’s stable and long-lasting, but generates only small amounts of power, with low efficiency. See TEG.
- RTI
- Real Time Interrupt.
- RTL
- (1)
- Run-time Library. A collection of standard functions and procedures to be added into programs at build time, if the programs are going to need them at runtime. This is known as static linking, and increases executable size. The newer approach is to link them dynamically, through a DLL. For example, the C function
strcpycompiles its code from the RTL into the executable, whilelstrcpy, which is the same function, is a DLL call – to the RTL DLL, in fact. - (2)
- Register Transfer Level. A description of hardware operations as data exchanges between registers. This view is commonly used in hardware description language (HDL) code, whether written in a specific register transfer language or a general-purpose language such as Verilog or VHDL. See GDS.
- (3)
- Register Transfer Language. A hardware description language for specifying CPU operations.
- (4)
- Recalled To Life. I hope you care to live?
- RTM
- Release To Manufacturing. The version of a commercial software release supplied to whoever packages it for end users – as CD, thumb drive, download, etc. It’s often made available to select users prior to the general release.
- RTOS
- Real Time Operating System. An OS designed to respond to events of its running program within short, specified time constraints. There are two general types: event-driven and time-sharing. Because it runs on the microcontrollers used in embedded devices, it needs to have a small footprint, i.e., be frugal with memory and code space.
- A system is soft real-time if it can tolerate some responses falling outside the expected time limit, and hard real-time if it can’t.
- The traditional approach to embedded programming is ad-hoc code written and compiled to run directly on a specific processor, with no OS. Programming to a RTOS instead, besides ensuring real-time response, simplifies and standardizes the coding process, aids reusability of code and middleware across different microcontrollers, and can even permit real-time multitasking. Because the typical microcontroller can run just one program, the compiler creates a single executable out of the RTOS and the source code.
- In 2001, Wind River’s VxWorks was market leader. As of 2011, it has many more rivals, most of them Linux-derived.
- RTP
- Real-Time Protocol. A transmission protocol that can be used instead of TCP when real-time forwarding (e.g. for voice & video) is more important than robust error-checking.
- RTS
- (1)
- Request To Send. See data protocol.
- (2)
- Real-Time Strategy. A class of computer strategy game in which players can’t pause the action.
- (3)
- Room-Temperature Superconductor. See HTS.
- RTSC
- Real-Time Software Components. An open-source project launched by the Eclipse Foundation (www.eclipse.org) to support component-based development of real-time embedded C and C++ software (firmware). Each RTSC component, or package, consists of one or more modules – collections of related C/C++ functions and types, plus JavaScript that monitors the code at runtime. Some hardware manufacturers, notably TI, have added RTSC to their tool sets.
- RTU
- Remote Terminal Unit. See SCADA.
- Ruby
- See programming language.
- RVDT
- Rotary Variable Differential Transformer. A sensor that measures angular rotation. It uses transformer coils and input current (usually AC) to generate an output voltage proportional to the rotation of its mechanical shaft, which makes it a type of transducer. Compare LVDT.
- RZ
- Return to Zero. As opposed to NRZ, this type of digital channel signaling is at 0V for the second half of each bit period. That means it has twice the signaling rate of NRZ at the same data rate, so its error performance suffers.
- Unipolar (or non-polar) RZ uses a positive voltage transitioning to 0V to represent binary 1, and is at 0V for the entire bit period to represent binary 0. Bipolar (or just polar) RZ instead uses a transition from a negative voltage to 0V to represent binary 0. Compare Manchester coding.
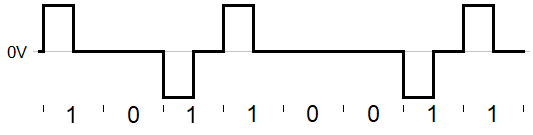
- RZ-AMI
- Return to Zero, Alternate Mark Inversion. The signaling standard for PCM. It’s a variant of RZ in which the mark (binary 1) waveform alternates between positive and negative forms, giving the signal a power spectral density (PSD) of zero.
| black | 0 |
| brown | 1 |
| red | 2 |
| orange | 3 |
| yellow | 4 |
| green | 5 |
| blue | 6 |
| violet | 7 |
| gray | 8 |
| white | 9 |

| ITU Band | Frequencies | Name | Communications Uses |
| n/a | < 3 Hz | none | none |
| 1 | 3-30 Hz | ELF (Extremely Low Frequency) | military submarine data |
| 2 | 30-300 Hz | SLF (Super Low Frequency) | military submarine data |
| 3 | 300-3000 Hz | ULF (Ultra Low Frequency) | subterranean data |
| 4 | 3-30 kHz | VLF (Very Low Frequency) | undersea data |
| 5 | 30-300 kHz | LF (Low Frequency) | longwave AM voice radio, information services |
| 6 | 300-3000 kHz | MF (Medium Frequency) | commercial AM radio, amateur radio |
| 7 | 3-30 MHz | HF (High Frequency) | commercial & amateur shortwave radio |
| 8 | 30-300 MHz | VHF (Very High Frequency) | heavily allocated; commercial FM radio & TV, aviation, marine |
| 9 | 300-3000 MHz | UHF (Ultra-High Frequency) | heavily allocated; mobile phones, microwave relay, satellites, TV, wireless networks |
| 10 | 3-30 GHz | SHF (Super-High Frequency) | lower range heavily allocated for same uses as UHF |
| 11 | 30-300 GHz | EHF (Extremely High Frequency) | some microwave relay; also 5G mobile phones |
| 12 | > 300 GHz | THF (Tremendously High Frequency) | none |


| RxD (from DCE) | TxD (to DCE) | GND | |
| DE-9 pin | 2 | 3 | 5 |
| DB-25 pin | 3 | 2 | 7 |
| RxD+ | RxD- | TxD+ | TxD- | GND | |
| DE-9 pin | 4 | 5 | 8 | 9 | 1 |
| DB-25 pin | 20 | 7 | 5 | 22 | 8 |